

- #Atropine antidote for manual
- #Atropine antidote for skin
Haddad and Winchester's clinical management of poisoning and drug overdose (Fourth ed.). Case report: Recurrent neonatal organophoshorus poisoning. Goldfrank's toxicologic emergencies (Tenth ed.). Indian Journal of Clinical Biochemistry, 27, 34-39. Regeneration of red cell cholinesterase activity following pralidoxime (2-pam) infusion in first 24 h in organophosphate poisoned patients. Goel, P., Gupta, N., Singh, S., Bhalla, A., Sharma, N., & Gill, K. Management of Acute Organophosphorous pesticide poisoning: Lancet, 371 (9612) (February), 597-604. Tucson, Arizona: The University of Arizona College of Medicine.Įddleston, M., Buckley, N.
#Atropine antidote for manual
(Ed.), AHLS advanced hazmat life support, provider manual (4th ed.). Quebec, Canada: Centre antipoison du Quebec.īorron, S. Antidotes en toxicologie d'urgence (3rd ed.).
Endpoint of therapy: Resolution of excessive bronchial secretions and symptomatic bradycardia.īailey, B., Blais, R., Gaudreault, P., Gosselin, S., & Laliberte, M. (2009). *After prolonged use of high doses of atropine it must be tapered gradually and reinstated if cholinergic symptoms recur. Initial infusion rates of 0.02 - 0.08 mg/kg/hour have been recommended (up to 2.4 mg/kg/hour has been required). Administration by infusion in severe cases may be considered. In severe organophosphate poisoning, very large doses and treatment for days to weeks have been necessary (total of 9 - 11 g over 30 - 40 days). Continue treatment until gradual reduction* in dose does not cause reappearance of cholinergic symptoms. 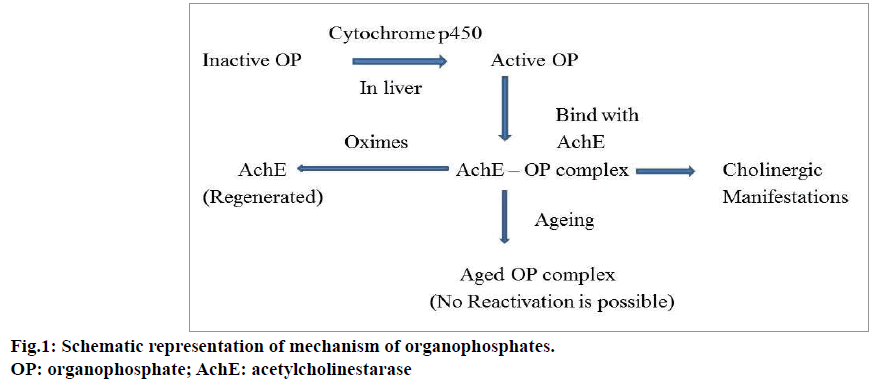
If no response, the dose is doubled every 5 - 10 minutes until tracheobronchial secretions are dry and patient can be oxygenated.

ORGANOPHOSPHATE, CARBAMATE AND MUSHROOM POISONING
Pralidoxime, in conjunction with atropine, should be used in the treatment of moderate to severe organophosphate poisonings and certain carbamate poisonings. Symptoms include excessive bronchial secretions leading to respiratory compromise, excessive oral and GI secretions, and bradycardia.
Reversal of cholinergic toxidrome due to organophosphate and carbamate insecticides, muscarine containing mushrooms, pilocarpine, choline esters. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for more information. This is not a complete list of atropine drug interactions. Tricyclic antidepressants such as trimipramine (Surmontil), amitriptyline (Elavil), nortriptyline (Pamelor, Aventyl), protriptyline (Vivactil), and clomipramine (Anafranil). Monoamine oxidase inhibitors such as tranylcypromine (Parnate), phenelzine (Nardil), selegiline (Eldepryl, Zelapar), isocarboxazid (Marplan), and rasagiline (Azilect). Methylphenidate (Concerta, Methylin, Ritalin). Benzodiazepines such as diazepam (Valium), lorazepam (Ativan), alprazolam (Xanax), and midazolam (Versed). Antipsychotics such as paliperidone (Invega), lurasidone (Latuda), olanzapine (Zyprexa), aripiprazole (Abilify), asenapine (Saphris), iloperidone (Fanapt), haloperidol (Haldol), prochlorperazine (Compazine), chlorpromazine (Thorazine), clozapine (Clozaril ), risperidone (Risperdal), quetiapine (Seroquel), and ziprasidone (Geodon). Antihistamines such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl). Anti-arrhythmia medications such as procainamide (Procanbid, Procan), disopyramide (Norpace, Rythmodan), quinidine, and digoxin (Lanoxin). Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Do not drive or operate heavy machinery until you know how atropine affects you. Atropine preparations for the eye may cause eye irritation, swelling of the eyelids, and sensitivity to light.Ītropine can also cause blurred vision, drowsiness, and dizziness. #Atropine antidote for skin
This medication is also available in injectable form to be given directly into a vein (IV) or muscle (IM) or directly under the skin (subcutaneously) by a healthcare professional.Ĭommon side effects of atropine include confusion, irregular heartbeat, increased heart rate, irritability, and fever. This medication comes in solution and ointment forms and is instilled in the eyes two to four times a day. These agents work by inhibiting the activity of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter in the nervous system. Atropine belongs to a group of drugs called anticholinergic agents. Atropine is also used to dilate the pupil before eye exams and to relieve pain caused by swelling and inflammation in the eye. Atropine is a prescription medication used to reduce salivation and bronchial secretions before surgery.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
